CrowdMap
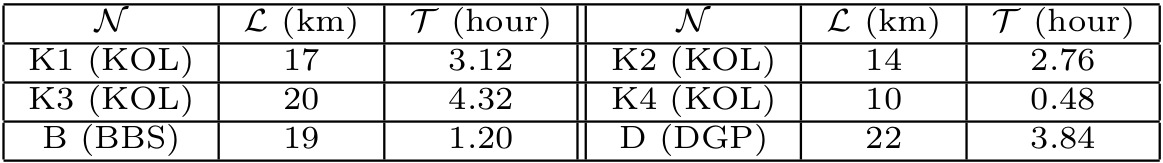
We conducted experiments for a period of three months in the cities of Kolkata (KOL), Bhubaneswar (BBS) and Durgapur (DGP), three cities in the eastern part of India. While KOL and BBS are two state capitals with areas 1887 sqkm and 422 sqkm respectively, DGP is a suburban city with area 154 sqkm.
The application was distributed amongst 30 users. The first month of the experiments involved logging the complete GPS information of these users, so that we can later use this information as ground truth. Also, they were asked to tag the mode of transport they were using and the landmarks encountered. The devices ranged from low-end Android devices to high-end ones. The Android versions ranged from JellyBean to Marshmallow. We conducted the experiments in 11 different routes of the above-mentioned cities and collected more than 200 trails.

In a nutshell, we have designed a low-cost solution that can provide useful information regarding road and route condition to users commuting in public transport in regions lacking Google transit information. We have implemented an Android based application as well as a web-interface to provide CrowdMap service to the commuters. With a 3-month study involving more than 30 users in 6 different bus-routes of 3 different cities, we observe that CrowdMap can detect landmarks with an average accuracy of 95% and embeds the route segments on real map with an maximum error of 5 meters. It can also accurately characterize the bus route characteristics like average speed, speed before landmark and jerkiness etc. To the best of our knowledge, this study is a first step towards developing a public transport recommender system based on users preference